

Here are 10 common types of error pattern, and the approximate age by which we expect them to be ‘fixed’ (gone) in typically developing children: 1. In English, we hear several common patterns of error in children’s speech as they grow up. As with any motor skill, children make plenty of mistakes as they learn to speak clearly.
AGE OF PHONOLOGICAL PROCESSES HOW TO
§ Typically eliminated by 2.Speech is a wonderfully complex skill, and children need lots of practice to learn how to do it. Denasalization – the substitution of a nasal consonant (“n” or “m”) with a non-nasal consonant (“b” or “d”) Reduplication – the repetition of a complete or incomplete syllable in substation for a wordģ. § Typically outgrown by age three but can linger until age nine in more severe cases of phonological delayĢ. Assimilation – when a consonant sound in a word starts to sound the same as another consonant in the word § The unstressed syllable is usually the one children eliminateĪssimilation processes: when sounds/syllables start to sound like surrounding soundsġ. Syllable reduction – the elimination of a syllable from a word that contains two or more syllables § Typically experienced by children with more sever phonological delaysĤ. Initial consonant deletion – the elimination of the beginning consonant of a word Final Consonant Deletion – the elimination of the final consonant in a wordģ. § Usually outgrown by 4 years old except for words starting with “s”Ģ. Cluster reduction – the reduction of a consonant cluster (two consonants next to one another) to one consonant Syllable Structure Processes: syllables are reduced, omitted or repeatedġ. Fronting - the term used when sounds that should be made in the back of the mouth (velar) are replaced with a sound made in the front of the mouth (alveolar) § Depending on the fricative sound this process is eliminated between the ages of three and sixĥ.
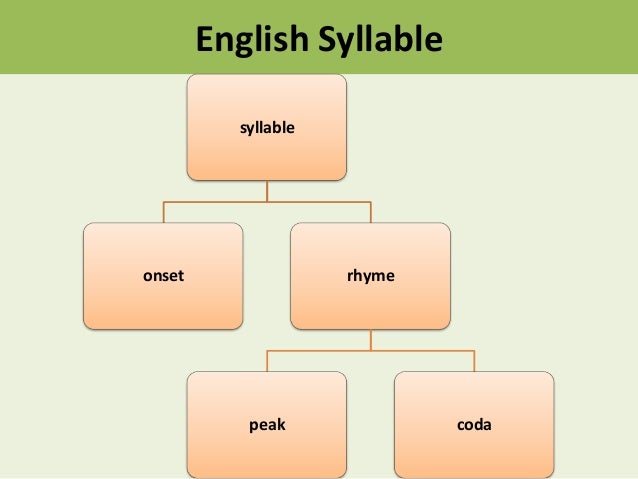
§ Age of elimination of this process varies from child to childĤ. Vowelization – the substitution of a vowel sound for “l” or “er” sounds § Typically only occurs in children with more sever phonological delaysģ. Backing – the substitution of a sound produced in the front of the mouth (like “t” or “n”) with a sound produced in the back of the mouth (like “k” or “g”) Gliding – the substitution of a liquid sound (typically letter “l” or “r”) with a glide sound (letters “w”, “y” or “j”)Ģ. Substitution Processes: replacing one class of sounds for another class of soundsġ. Speech-Language Pathologists (Profession) Speech-Language-Hearing Assessments (Assessment category) Please include attribution to with this graphic. By age five most children naturally outgrow their use of phonological error patterns.Ĭlick here for a printer-friendly version of this infographic They do this because they lack the ability to appropriately coordinate their lips, tongue, teeth, palate and jaw for clear speech. Phonological processes: patterns of sound errors that typically developing children use to simplify speech as they are learning to talk.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
